Traffic Analysis Practise: IcedID & Trickbot
Working on another challenge from malware-traffic-analysis.net.
I've been provided with a .pcap file of network traffic and a .jpg showing a bunch of IDS alerts.
10.2.23.231
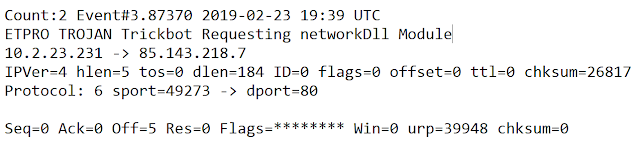
The IP was displayed in the alerts as shown in the image below.
00:11:0a:9f:c0:2d (HewlettP_9f:c0:2d)
I found the MAC address in the Ethernet section of the NetBIOS Name Service packet.
What is the host name of the infected Windows host?
FERGUSON-WIN-PC
I found the host name in the NetBIOS Name Service packet.

What is the Windows user account name for the infected Windows host?

What is the Windows user account name for the infected Windows host?
ruby.ferguson
I found the user account name by filtering the packets with "kerberos.CNameString". I then added CNameString results as a column which quickly showed me which packets had the windows user account name in them.
What are the six URLs that returned Windows executable files to the infected Windows host?
- http://209.141.55.226/troll1.jpg
- http://46.249.62.199/Tinx86_14.exe
- http://46.249.62.199/Sw9JKmXqaSj.exe
- http://85.143.218.7/win.png
- http://85.143.218.7/tin.png
- http://85.143.218.7/sin.png
I found the URLs using the export HTTP objects feature in Wireshark. I noted the IPs and messages from the IDS alerts and cross-referenced them with the listed HTTP objects to find the packets containing suspicious files.
I double checked the URLs by filtering on the IPs, for example "ipaddr == 209.141.55.226 && http".
You can tell the "image" sent is actually an executable file by following the TCP stream. You can see the first two bytes of the file are MZ which is consistent with an EXE or DLL file.
Based on the IDS alerts, what type of infection (or infections) is this?







Thanks for the great information you have provided! Leather Biker Vest
ReplyDelete